Headings
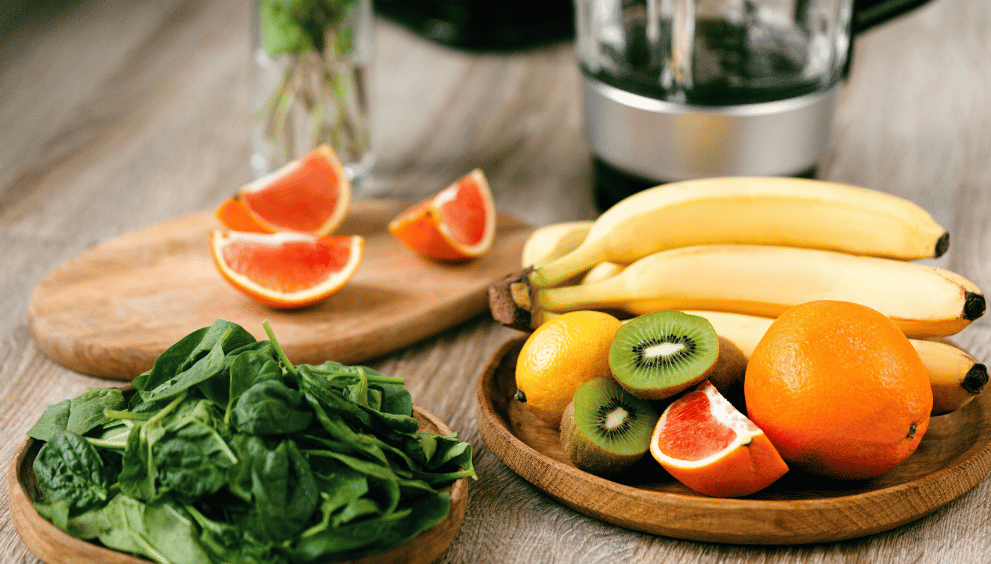
Maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle is crucial for obtaining all the nutrients our bodies need. For this reason, it is essential to categorize foods correctly and understand the role of each food group in developing healthy eating habits. Here are the 7 essential food groups that form the foundation of healthy eating:
1. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. As a food group, they are found in two primary forms: simple and complex carbohydrates.
- Simple Carbohydrates: These are sugars that provide quick energy. They can be found in fruits, honey, and dairy products.
- Complex Carbohydrates: These provide longer-lasting energy and are rich in fiber. Whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and some fruits belong to this food group.
Carbohydrates are essential for the proper functioning of bodily functions. They also enhance mental performance, supporting concentration and focus.
2. Proteins
Proteins are essential food groups necessary for cell repair, growth, and overall bodily functions.
- Animal Proteins: These are found in foods such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. This food group contains all essential amino acids.
- Plant Proteins: These are sources of protein found in legumes, nuts, seeds, and some grains. Plant proteins may lack some essential amino acids, so it’s important to diversify your sources.
Adequate protein intake supports muscle development and strengthens the immune system. It also promotes satiety, aiding in weight control.
3. Fats
Fats are an important food group that helps the body store energy, produce hormones, and absorb vitamins.
- Healthy Fats: Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in foods like olive oil, avocado, walnuts, and hazelnuts support heart health.
- Saturated Fats: It’s recommended to limit the intake of saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy products.
Fats play a critical role in meeting the body’s energy needs, as well as being essential for cell structure. Additionally, healthy fats like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids support brain function and reduce inflammation.
4. Vitamins
Vitamins are organic compounds necessary for the healthy functioning of the body. Different types of vitamins can be obtained from various food groups:
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble and are typically found in fatty foods.
- Water-Soluble Vitamins: Vitamins C and B are found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Vitamins are essential for the immune system, energy production, and overall health. Sufficient vitamin intake enhances your resistance to diseases.
5. Minerals
Minerals are inorganic compounds that support various functions in the body. Important food groups include:
- Calcium: Necessary for bone health, found in dairy products and leafy green vegetables.
- Iron: Found in red blood cells, iron is present in meat, legumes, and nuts.
Minerals are vital for maintaining a healthy life. Adequate mineral intake supports your overall health and optimizes many bodily functions.
6. Fiber
Fiber is an important food group that supports the healthy functioning of the digestive system. There are two types of fiber:
- Soluble Fiber: Found in foods like oats, lentils, and apples, it helps balance blood sugar levels.
- Insoluble Fiber: Found in whole grains, vegetables, and legumes, it eases digestion and supports intestinal health.
Sufficient fiber intake regulates the digestive system and provides a feeling of fullness. It also supports heart health and can reduce the risk of colon cancer.
7. Water
Water is a vital necessity and is essential for all life functions.
- Hydration: Water is necessary for all chemical reactions in the body. Drinking adequate amounts of water helps maintain the body’s water balance.
- Detoxification: Water assists in flushing toxins from the body.
Increasing daily water intake is an essential step to support a healthy lifestyle. Proper hydration boosts energy levels and enhances mental performance.
Importance of Healthy Eating
Eating healthily not only helps maintain your overall health but also improves your quality of life. Here are some benefits of healthy eating:
- Weight Control: A balanced diet helps in healthy weight gain and maintenance.
- Disease Prevention: It reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
- Energy Levels: Healthy eating increases your energy levels, helping you stay alert throughout the day.
- Mental Health: Good nutrition improves your mood and supports your mental health.
Healthy Eating Tips
To establish a healthy food group regimen, consider the following tips:
- Plan Ahead: Prepare a weekly meal plan to think about healthy meals in advance.
- Choose Fresh Foods: Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables instead of processed foods.
- Portion Control: Monitor your portions to reduce the risk of overeating.
Conclusion
These 7 essential food groups form the foundation of healthy living. A balanced diet ensures that you receive all the nutrients your body needs and helps you maintain a healthy lifestyle. Understanding the role of each food group and incorporating them into your daily diet is one of the most effective ways to protect your health. Remember, healthy living is not only about physical health but also about mental and emotional balance. Therefore, you can achieve a higher quality of life by developing healthy eating habits.
Expanded Content
1. Carbohydrates
Details about carbohydrates:
- Whole Grains: Whole grains like oats, quinoa, and brown rice provide energy and are rich in fiber. These foods help regulate the digestive system and promote a feeling of fullness.
- Fruits and Vegetables: These foods are not only sources of carbohydrates but also rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. It is recommended to consume at least 5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily.
2. Proteins
More information about proteins:
- Protein Sources: A variety of protein sources, including fish, chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes, are available. Daily adequate protein intake is vital for muscle development and repair.
- Amino Acids: The body uses 20 different amino acids. Nine of these are essential amino acids that cannot be synthesized by the body. These amino acids should be obtained from adequate protein intake.
3. Fats
Details about the types of fats and their benefits:
- Omega-3 and Omega-6: These fatty acids are crucial for heart health and brain function. Good sources include salmon, walnuts, and chia seeds.
- Monounsaturated Fats: Foods like olive oil and avocados are rich in monounsaturated fats, which can help reduce bad cholesterol levels.